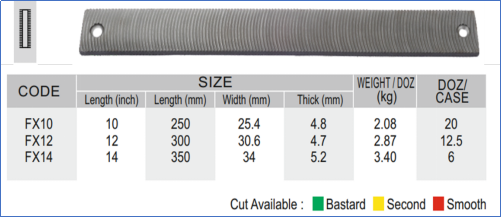
These files are utilized for quick metal removal. The cross section is rectangular, with one edge single-cut and the sides double-cut.
Mittal Files & Tools Pvt.Ltd. founded & guided under the leadership of Mr. N.K. Mittal in 2010, is today India's 2nd largest manufacturer of Steel files and Agriculture tools, with an annual capacity of over 30 million pieces per annum.
Read More

Mittal Files & Tools Pvt. Ltd. established in 2010, is today India's 2nd largest manufacturer of Steel files and Agriculture tools, with an annual capacity of over 30 million pieces per annum.
Mittal Files & Tools Pvt. Ltd. has three manufacturing facilities in India producing wide range of steel files with over 2 million pieces each month as per International Standards like I.S.S, B.S.S, F.S.S, D.I.N & J.S.S that meet our Customers' requirement by committing to ensure consistent quality, timely delivery & satisfying customary needs of the times.
Mittal Files & Tools Pvt. Ltd. has its Global presence and is strengthening its International footprints through exports to over 33 major countries in North, South and Latin America, Central & South Africa, South Asia, South-East Asia, Europe & Middle East accounting 90% of its total sales .
Round Chain Saw, Flexible File, Rigid Type, Tungsten Point, Needle File, Diamond File
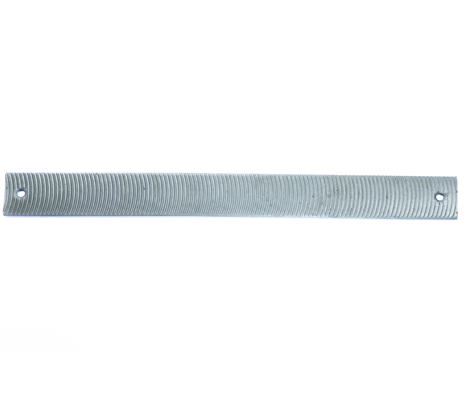
A Flexible Metal file is a type of hand tool used for shaping and smoothing various materials, particularly metal. It consists of a long, narrow piece of metal with a rough surface, designed to remove small amounts of material through abrasion. The flexibility of the file allows it to conform to the contours of the workpiece, making it especially useful for working on curved or irregular surfaces.
Material:z The flexibility allows the file to bend slightly, enabling it to follow the contours of the workpiece. Useful for working on concave or convex surfaces where rigid files may not be effective.
Surface Texture : Available in different grades of coarseness, from very fine to very coarse, to suit various applications. The texture is created through a process called "cutting" or "etching," where grooves are formed on the surface of the file.
Shapes and Sizes: Come in various shapes such as flat, round, half-round, and triangular. Sizes vary, typically ranging from small precision files to larger, more robust files for heavy-duty work.
Handles:Often equipped with a handle made of wood, plastic, or rubber to provide a comfortable and secure grip.
Flexible metal files, also known as flexible rasps or bending files, are versatile tools used in various applications where traditional rigid files may not be practical. Here are some common uses and advantages of flexible metal files:
Shaping and Smoothing Curved Surfaces:Ideal for working on curved or irregular surfaces where a rigid file cannot conform. Commonly used in automotive bodywork, model making, and woodworking to shape and smooth edges.
Finishing WorkUsed to remove burrs, sharp edges, and excess material from metal, plastic, or wood surfaces. Ensures a smooth, finished look on detailed and intricate workpieces..
Tool and Die Making:Essential in tool and die shops for precision work on molds and dies. Allows for fine adjustments and detailed finishing on complex shapes.
Jewelry Making: Used for detailed work in jewelry making, such as shaping metal or smoothing solder joints. Provides the flexibility needed to work on small and delicate pieces.
Metalworking and Fabrication: Useful for deburring and finishing welds or metal joints. Helps in achieving smooth transitions and clean finishes on fabricated parts.
Flexibility Can bend to fit the contours of the workpiece, providing consistent contact and more effective material removal. Reduces the risk of gouging or damaging the surface compared to rigid files.
VersatilityAdaptable to a variety of materials, such as wood, plastic, and metal. accessible in a range of sizes and forms to meet a variety of demands and applications.
Precision: Allows for controlled, precise filing, especially in tight or hard-to-reach areas. Ideal for delicate work requiring careful material removal.
Comfort and Ergonomics: Often designed with ergonomic handles to reduce hand fatigue during prolonged use. The flexible nature of the file can make it easier to use with less effort compared to rigid files.
These files are utilized for quick metal removal. The cross section is rectangular, with one edge single-cut and the sides double-cut.

Cleaning: Regularly clean the file with a wire brush or file card to remove metal shavings and debris. Avoid clogging by using chalk or soap on the file before use, which helps to prevent metal particles from sticking.
Storage: Store files in a dry place to prevent rusting. Keep them in a protective case or wrapped in cloth to avoid damage to the cutting surfaces.
Usage Use the appropriate file for the material and task at hand. Apply even pressure and use long, smooth strokes to maintain the file's effectiveness and longevity.
Jewelry Making: Jewelers use precision flat files for shaping and finishing metals such as gold, silver, and platinum in jewelry manufacturing and repair.
Die and Mold Making: Tool and die makers, mold makers, and machinists use flat machinist files to refine surfaces and achieve precise dimensions in the production of dies, molds, and tooling.
Die and Mold Making: Tool and die makers, mold makers, and machinists use flat machinist files to refine surfaces and achieve precise dimensions in the production of dies, molds, and tooling.
Instrument Making: Instrument makers, such as those crafting musical instruments or precision scientific instruments, use flat machinist files for shaping and finishing metal components to exact specifications.
Model Making and Hobbyist Crafts: Hobbyists and model makers use flat machinist files for shaping and detailing various materials in crafting scale models, miniatures, and other hobbyist projects.
Plastics Fabrication: Plastic fabricators and molders use flat machinist files for shaping and finishing plastic components and molds in industries such as packaging, consumer goods, and electronics.
Construction: Construction workers and contractors may use flat machinist files for tasks such as shaping metal brackets, smoothing rough edges, and fitting parts in construction projects.
